Appearance
Programming Models
Depending on the selected environment and supported language, you have the choice of different Programming Models. If possible, choose The Recommended Path, but this can differ for costs, knowledge or other reasons.
Cloud Environment
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Fiori Application Programming Model | Building blocks of reusing existing SAP services to build up new Business Solutions. |
| SAP Cloud Application Programming Model (CAP) | Framework of languages, libraries, and tools for building enterprise-grade services and applications. It guides developers along a ‘golden path’ of proven best practices and a great wealth of out-of-the-box solutions to recurring tasks. |
| SAP Cloud SDK | Versatile set of libraries and tools for developers to build applications in a cloud-native way and deliver them via the SAP BTP. |
ABAP Environment
Evolution of the ABAP Programming Models
The ABAP platform development team evolutionary enhanced the way of development, especially for SAP Fiori Elements.
| Model | Platform | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model (RAP) | SAP BTP ABAP Environment or SAP S/4HANA ≥ 7.54 (1909) | Defines the architecture for efficient end-to-end development of intrinsically SAP HANA-optimized OData services (such as Fiori apps) in SAP BTP ABAP Environment or Application Server ABAP. Evolutionary successor of the ABAP Programming Model for SAP Fiori. |
| The ABAP Programming Model for SAP Fiori (BOPF) | ABAP Platform ≥ 7.5 | Based on modern and proven technologies such as CDS, BOPF and SAP Gateway. A lightweight CDS-based flavor of the BOPF framework is used in this context for the transactional processing. |
| Classic ABAP Application Programming | ABAP Platform ≤ 7.5 | With the ABAP release 7.4, SAP started to heavily optimize the ABAP platform for its in-memory database SAP HANA. In this context ABAP Core Data Services (CDS) were introduced to offer the next generation data modeling infrastructure and data access. CDS-based data models are semantically rich data models that can be used for all application domains. Additionally, SAP Gateway became an integral part of the AS ABAP with release 7.4 and the Business Object Processing Framework (BOPF). |
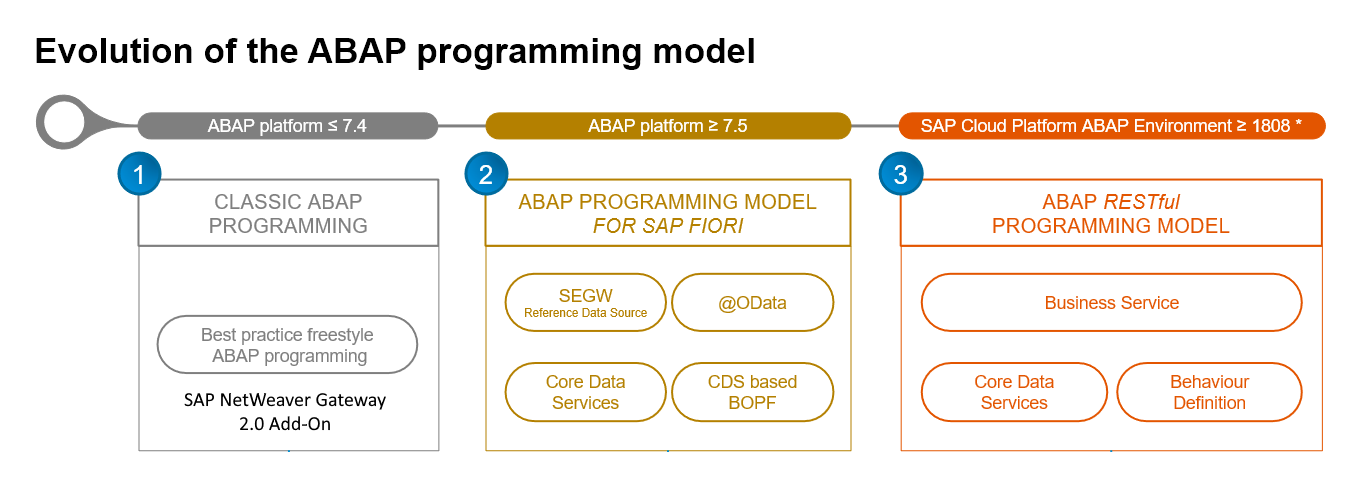
The ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model is the evolutionary successor of the ABAP Programming Model for SAP Fiori. It is generally available to customers and partners within SAP Cloud Platform ABAP Environment starting with release 1808 and within ABAP Platform starting with release 7.54 SP00 (1909 FPS00).
ABAP RESTful SAP S/4HANA On-Premise release dependencies
- Managed runtime implementation type (Greenfield) is available with SAP S/4HANA ≥ 2020
- OData v4 service binding is available with SAP S/4HANA ≥ 2020 FPS01
ABAP Platform for SAP S/4HANA 2021
With the 2021 release, the ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model (RAP) closed open gaps (like unmanaged early numbering) and is the recommended path (currently best practise).
See the Overview and Product Highlights and read the blog ABAP Platform for SAP S/4HANA 2021 containing regularly updated ABAP Platform news.
Feature Availability Matrix
Compact overview of ABAP Programming Model from (Andre Fischer Blog).
| GW V2 | GW V4 | BOPF | RAP | RAP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Release | ≥7.0 | ≥7.52 | ≥7.51 | SAP BTP ABAP Environment | SAP S/4HANA ≥1909 |
| Greenfield implementation | + | + | + | + | ≥2020 FSP1 |
| Brownfield implementation | + | + | − | + | + |
| OData V2 | + | − | + | + | + |
| OData V4 | − | + | − | + | ≥2020 FSP1 |
| Draft handling | − | − | + | + | ≥2020 FSP1 |
| Multi-Inline-Edit | − | − | + | + | − |
| Asynchronous OData V4 Requests | − | + | − | + | ≥2020 FSP1 |
| Backend annotations in CDS views | (+) | − | + | + | + |
| Backend annotations using code based implementation | + | + | (+) | − | − |
| Local annotations in SAP Fiori Tools | + | + | + | + | + |
(+) When using Referenced Data Source Approach (RDS)
Implementation types
| Greenfield (managed) | Brownfield (unmanaged) |
|---|---|
| With greenfield implementation we mean scenarios where no legacy coding is called. Such scenarios are also called managed since in this case the underlying framework takes care of all create, update and delete requests and stores them in the database. | With brownfield implementation we mean scenarios where existing legacy code such as a BAPI is being called by your service implementation in order to store the changed data in the database. Such scenarios are also called unmanaged. Another name for such scenarios are managed scenarios with a self implemented save. |
SAP Gateway
SAP Gateway Foundation (SAP_GWFND) is a software component which is available within SAP NetWeaver ≥ 7.5. Previous NetWeaver releases need the optional SAP NetWeaver Gateway 2.0 Add-On.
The Gateway Foundation consists of the core components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| GW_CORE | OData libraries |
| IW_FND | Runtime component, metadata store, shared services |
| IW_BEP | Business enablement provisioning |
| IW_HDB | Business content adapter for SAP Gateway with SAP HANA to enable exposure of SAP HANA views |
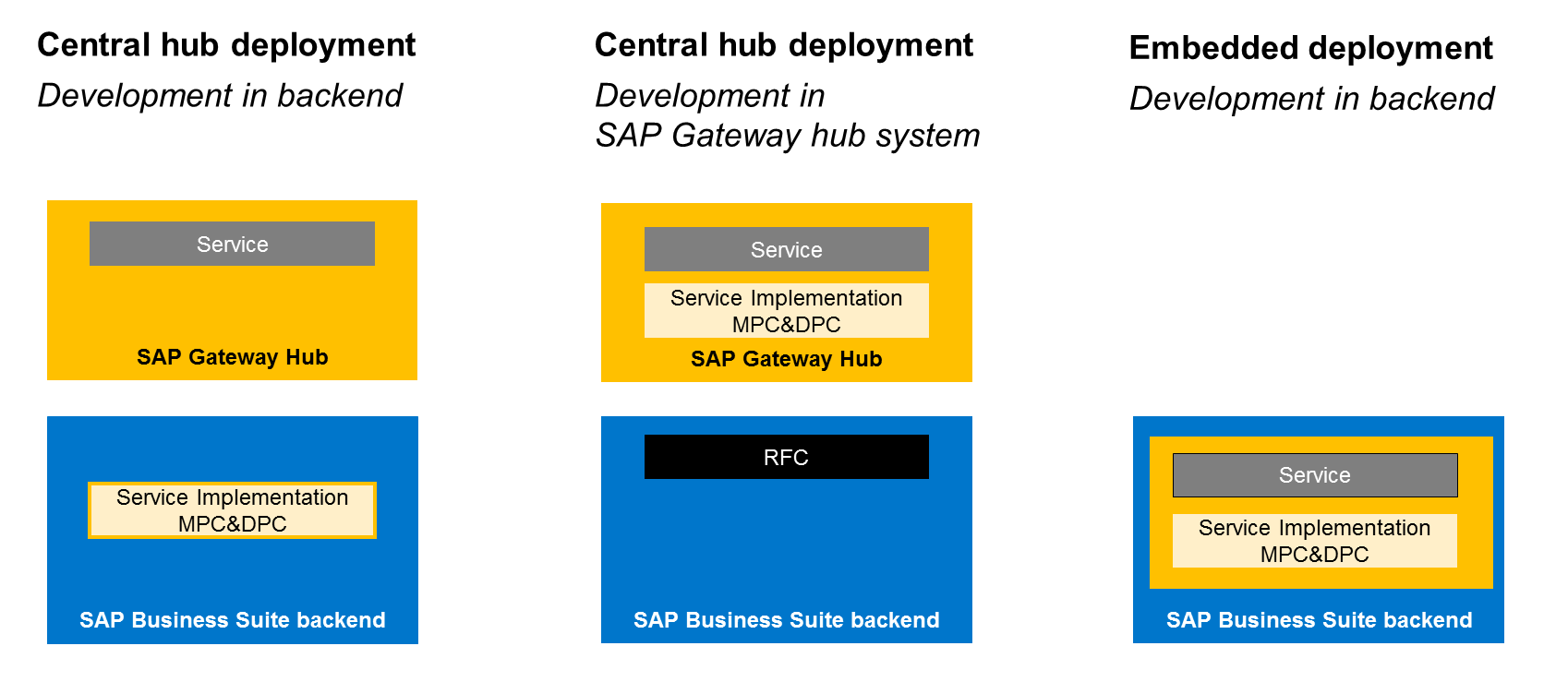
Deployment Options
Depending on your preferred system landscape, different deployment options are available for SAP Gateway Foundation:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Central Hub Deployment | Service development in the SAP Business Suite backend system |
| Central Hub Deployment | Service development in SAP Gateway Foundation hub system |
| Embedded Deployment | Service development in the SAP Business Suite system |
The following graphic provides a simplified overview of the different deployment options: